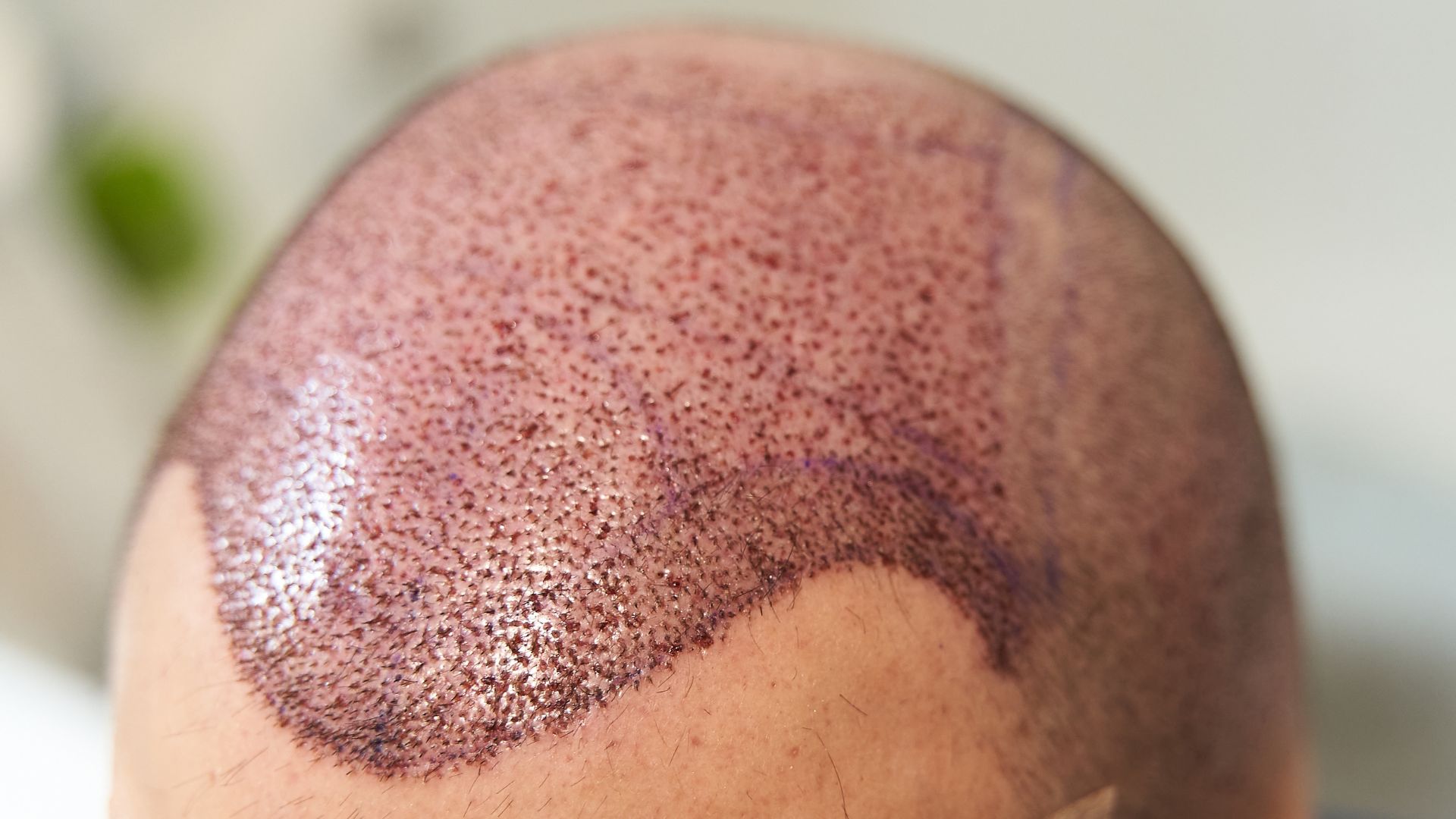
Key Takeaways: Hair Graft Procedure
| Key Aspects | Detailed Takeaways |
|---|---|
| Overview of Hair Grafting | Hair grafting, also known as hair transplantation, is a surgical procedure to treat hair loss. The evolution from early techniques to modern FUT and FUE methods has significantly improved outcomes. |
| Preoperative Considerations | Suitable candidates are selected based on hair density and baldness patterns. Realistic expectations and a thorough consultation with a surgeon are essential. Preoperative preparations include stopping certain medications and lifestyle adjustments. |
| The Hair Grafting Process | FUT involves removing a strip of scalp, while FUE extracts individual follicles. Both require anesthesia, careful graft preparation, and postoperative care to ensure success. |
| Postoperative Care | Aftercare includes detailed instructions for home care, managing common symptoms like swelling and discomfort, and avoiding activities that could damage grafts. |
| Benefits of Hair Grafting | Hair grafting offers cosmetic improvements and psychological benefits such as increased self-esteem. Results are long-lasting and can look very natural. |
| Risks and Complications | Common side effects include swelling and bruising. Complications can range from infection to graft failure, but preventative measures and treatments are available. |
| Recovery and Aftercare | Immediate recovery involves managing pain and swelling, while long-term recovery focuses on hair growth and final results. Lifestyle adjustments post-transplant are crucial for maintaining graft health. |
| Cost and Insurance Coverage | Costs are influenced by the extent of hair loss, number of grafts, and chosen technique. Hair grafting is typically not covered by insurance, but financing options may be available. Long-term benefits should be weighed against upfront costs. |
Difference between Hair Graft and Hair Transplant
| Aspect | Hair Grafting | Hair Transplantation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Refers specifically to the individual units of hair that are moved during surgery. | Refers to the overall surgical procedure of moving hair from one part of the body to another. |
| Focus | Primarily concerned with the extraction and preparation of hair units. | Encompasses the entire process, including extraction, preparation, and placement of hair grafts. |
| Procedure Detail | Involves the scoring and handling of hair grafts to ensure their viability. | Includes not only the handling of grafts but also the planning of the recipient area, anesthesia, and post-operative care. |
| Techniques Involved | Limited to the methods of obtaining the grafts, such as FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction) or FUT (Follicular Unit Transplantation). | Includes both the techniques for harvesting grafts and the techniques for implanting them into the recipient area. |
| Outcome | The quality and survival of the hair grafts are the main concerns. | The overall aesthetic and functional success of the hair restoration, including the natural appearance and health of the transplanted hair. |
Table of Contents
Introduction
Hair grafting, commonly referred to as hair transplantation, is a medical procedure aimed at restoring hair in areas affected by baldness or thinning. This surgical technique has evolved significantly over the years, offering hope and renewed confidence to individuals experiencing hair loss. In this blog, we’ll delve into the intricacies of hair grafting, its history, and the primary methods used today. We’ll also discuss the critical preoperative considerations that candidates must be aware of before undergoing the procedure.
Overview of Hair Grafting
Hair grafting is a surgical intervention that involves transferring hair follicles from a part of the scalp with ample hair, known as the donor site, to the balding or thinning areas, referred to as the recipient sites. This process not only aims to restore hair growth in areas affected by hair loss but also to do so in a manner that appears natural and seamless.
Brief History of Hair Grafting Techniques
The journey of hair grafting techniques has been marked by continuous advancements:
- Early Beginnings: The concept of hair transplantation dates back to the 19th century, with rudimentary procedures that were far from the sophisticated methods used today7.
- Mid-20th Century: Modern hair transplantation began in the 1950s with the pioneering work of Dr. Norman Orentreich, who introduced the concept of donor dominance, proving that transplanted hair could maintain its characteristics and resist balding812.
- Evolution: Over the decades, hair grafting has transitioned from the use of larger grafts, which often resulted in an unnatural appearance, to the refined techniques of today that prioritize aesthetic outcomes47.
Primary Methods of Hair Grafting
There are two main techniques for hair grafting:
- Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT):
- Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE):
Preoperative Considerations
Before undergoing hair grafting, several preoperative considerations must be taken into account:
Criteria for Selecting Suitable Candidates
- Age: Ideal candidates are typically over the age of 25, as hair loss patterns are more predictable at this stage6.
- Hair Loss Pattern: Men with the Norwood pattern and women with the Ludwig pattern of hair loss are good candidates6.
- Hair Density: A higher density of hair follicles in the donor area often leads to better coverage6.
- Hair Color: Individuals with hair color similar to their skin tone may experience more natural-looking results6.
Importance of Realistic Expectations
- Consultation: A thorough consultation with a surgeon is essential to understand the procedure, potential outcomes, and limitations.
- Expectation Management: Patients must have realistic expectations regarding the results of the hair grafting procedure.
Preoperative Preparations
- Medications: Patients may need to stop taking certain medications that could affect the surgery’s outcome14.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Lifestyle changes, such as quitting smoking and avoiding alcohol, may be recommended to improve the healing process14.
By understanding these aspects of hair grafting, candidates can make informed decisions and prepare adequately for the procedure, increasing the likelihood of a successful outcome.
The Hair Grafting Process
Hair grafting, whether through Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) or Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE), involves several meticulous steps to ensure the successful transplantation of hair. Below, we detail the processes involved in both methods, highlighting the differences and similarities in their approaches.
Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) Procedure
- Preparation and Anesthesia:
- The patient’s scalp is cleaned and local anesthesia is administered to numb the donor area1.
- A sedative may also be given to help the patient relax during the procedure.
- Donor Hair Harvesting:
- A strip of scalp is surgically removed from the back of the head using a scalpel19.
- The area is then sutured closed, leaving a linear scar that is typically concealed by the patient’s remaining hair.
- Graft Preparation:
- The excised strip of scalp is carefully dissected under a microscope into individual follicular units or grafts, each containing 1 to 4 hairs10.
- Transplantation:
- The recipient area is prepared by making tiny incisions or slits in the scalp.
- The follicular unit grafts are meticulously inserted into these incisions in a predetermined density and pattern to mimic natural hair growth9.
- Immediate Postoperative Care:
- The scalp is typically not bandaged, but patients are given instructions on how to care for their scalp3.
- Swelling and mild discomfort may occur, which can be managed with prescribed medications.
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) Procedure
- Preparation and Anesthesia:
- Donor Hair Harvesting:
- Instead of removing a strip of scalp, a specialized punch tool is used to extract individual follicular units directly from the scalp18.
- This method leaves small, round scars that are less noticeable and do not require suturing.
- Graft Preparation:
- Extracted grafts are kept in a preservation solution to maintain their viability until transplantation10.
- Transplantation:
- The recipient area is prepared similarly to the FUT method, with tiny incisions made to accommodate the grafts.
- The grafts are then individually inserted into these incisions18.
- Immediate Postoperative Care:
- Postoperative care is similar to FUT, with instructions on how to care for the transplant site to prevent infection and ensure optimal growth3.
- Patients may experience less discomfort and a quicker recovery time compared to FUT due to the less invasive nature of the harvesting technique.
Comparison Table: FUT vs. FUE
| Feature | FUT | FUE |
|---|---|---|
| Scarring | Linear scar at donor site | Multiple small, round scars at donor site |
| Procedure Time | Longer due to strip extraction and suturing | Shorter per session, may require multiple sessions |
| Recovery | Longer due to the surgical nature of the donor site | Quicker recovery with minimal postoperative discomfort |
| Cost | Generally less expensive due to fewer sessions | May be more expensive due to the labor-intensive nature of the procedure |
| Best for | Patients who need a large number of grafts and prefer a single session | Patients who prefer a less invasive method and minimal scarring |
Postoperative Bandaging and Care
- Bandaging: Typically, no tight bandaging is required for FUE, while FUT might require minimal bandaging to protect the linear incision3.
- Care Instructions: Patients are advised to avoid strenuous activities and direct sunlight, and to follow a gentle washing regimen to prevent dislodging of the grafts311.
- Medication: Pain relief medications and antibiotics may be prescribed to manage discomfort and prevent infection3.
This detailed approach to hair grafting ensures that patients are well-informed of the procedures and can make the best decisions for their hair restoration goals.
Postoperative Care
After undergoing a hair graft procedure, whether FUT or FUE, proper postoperative care is crucial to ensure the success of the transplant and the health of the patient. This section provides detailed guidance on how to care for the scalp following the surgery, what symptoms to expect, and what activities to avoid.
Detailed Aftercare Instructions
Patients are given specific instructions to follow at home to facilitate healing and optimize the outcome of the hair transplant. These include:
- Scalp Care:
- Keep the scalp dry on the first day to allow the skin to start healing.
- From the second day, gently wash the transplanted area with mild shampoo to prevent scabs from forming around the hair shafts.
- Avoid direct water pressure on the transplanted grafts; instead, use a cup to gently pour water over the area.
- Sleeping Position:
- Sleep with your head elevated on pillows for the first few nights to minimize swelling.
- Try to sleep on your back to avoid rubbing the transplanted area against pillows.
- Medications:
- Take prescribed antibiotics to prevent infections and anti-inflammatory medications to manage swelling.
- Pain medications should be taken as prescribed if discomfort is significant.
Common Postoperative Symptoms and Management
Postoperative symptoms are typically mild and manageable. Here are some common symptoms and tips on how to handle them:
| Symptom | Management |
|---|---|
| Swelling | Use cold compresses and keep the head elevated, especially when sleeping. |
| Pain and Discomfort | Over-the-counter pain relievers can be used as directed by the surgeon. |
| Itching | Keep the area clean and avoid scratching. Antihistamines may be recommended. |
| Redness and Tenderness | Usually resolves on its own, but contact your surgeon if it persists or worsens. |
Activities to Avoid During the Recovery Period
To ensure the survival of the grafts and promote optimal healing, patients are advised to avoid certain activities:
- Physical Activities:
- Avoid strenuous activities such as jogging, cycling, and gym workouts for at least a week.
- Heavy lifting and bending over should be avoided to reduce the risk of bleeding and swelling.
- Environmental Exposure:
- Stay out of direct sunlight and avoid swimming in chlorinated pools or the sea for at least a month.
- Avoid dusty environments and any situation where the scalp could become dirty or sweaty.
- Hair Care:
- Do not use chemical treatments such as dyes, perms, or straighteners for at least six weeks.
- Avoid brushing or combing over the grafts for the first few weeks.
- Diet and Lifestyle:
- Smoking and drinking alcohol should be avoided as they can impair the healing process.
- Maintain a healthy diet rich in vitamins and minerals to support wound healing and hair growth.
Following these detailed aftercare instructions and managing common postoperative symptoms effectively are key to a successful recovery from a hair graft procedure. Patients should always follow their surgeon’s advice and attend follow-up appointments to ensure the best outcomes.
Benefits of Hair Grafting
Hair grafting is not just a medical procedure but a transformative experience for many who undergo it. The benefits extend beyond the physical aspects, significantly impacting psychological well-being and quality of life. Here, we explore both the cosmetic and psychological benefits, as well as the longevity and natural appearance of hair grafting results.
Cosmetic and Psychological Benefits
Improvement in Appearance
- Hair Fullness and Coverage: Hair grafting effectively increases the density of hair in thinning areas, providing a fuller head of hair. This is particularly beneficial for those with noticeable bald spots or receding hairlines.
- Youthful Appearance: Restoring hair can make individuals look younger, which is often an important factor for those who feel that balding has aged them prematurely.
Psychological Benefits
- Increased Self-Esteem and Confidence: Many patients report a significant boost in self-esteem and confidence following hair grafting. The ability to style their hair and not worry about concealing baldness can lead to improved social interactions and personal satisfaction.
- Reduced Anxiety and Depression: For some, balding can lead to anxiety and depression. Restoring hair can alleviate these feelings by addressing one of the root causes of their distress.
Longevity of Results
Permanence of Hair Grafting
- Lasting Results: Once the transplanted hair follicles establish themselves, the results can be permanent. The transplanted hair typically continues to grow like normal hair.
- Factors Influencing Success Rate:
- Donor Hair Quality: The quality and density of the donor hair can significantly affect the outcome.
- Technique Used: The skill of the surgeon and the chosen technique (FUT vs. FUE) also play critical roles in the success of the transplant.
Natural-Looking Outcomes
- Technological Advancements: Modern hair grafting techniques, such as advanced FUE and micro grafting, allow for the placement of hair follicles in a way that matches the natural growth pattern of the surrounding hair.
- Artistry of Surgeon: The surgeon’s ability to artistically place hair grafts at the correct angle and density is crucial for achieving a natural-looking hairline.
Summary Table: Benefits of Hair Grafting
| Benefit Type | Details |
|---|---|
| Cosmetic Improvements | Enhanced hair fullness, coverage, and a more youthful appearance. |
| Psychological Boost | Increased self-esteem, confidence, and reduced anxiety related to appearance. |
| Longevity and Naturalness | Permanent results with natural-looking outcomes due to advanced techniques. |
Hair grafting offers a comprehensive solution not only for hair loss but also for the emotional and psychological challenges that often accompany it. The procedure’s ability to deliver long-lasting and natural-looking results further underscores its value as a worthwhile investment in one’s appearance and mental health.
Risks and Complications
While hair grafting is generally safe, like any surgical procedure, it comes with potential risks and complications. Understanding these risks and knowing how to manage them can help ensure a smoother recovery and better overall outcomes.
Common Side Effects
Short-Term Side Effects
- Swelling: Often occurs around the forehead and may last a few days.
- Bruising: Can appear around the eyes and forehead, typically subsiding within a week.
- Discomfort: Mild to moderate pain which can usually be managed with over-the-counter pain relievers.
Shock Loss
- Temporary Shedding: Some of the transplanted or even existing hair may temporarily shed due to trauma from the surgery. This is typically temporary, and hair usually begins to regrow within a few months.
Possible Complications
Risks of Infection, Bleeding, and Scarring
- Infection: While rare, it can occur if postoperative care instructions are not properly followed.
- Bleeding: Minimal bleeding is expected during and after surgery, but excessive bleeding can occur.
- Scarring: FUT method may leave a linear scar, and FUE can leave small round scars at the extraction sites.
More Serious Complications
- Graft Failure: Occurs when the transplanted hair follicles do not survive.
- Unnatural Hair Growth Patterns: Can result if grafts are not placed correctly.
- Folliculitis: Inflammation of the hair follicles, which can cause discomfort and affect the appearance of the transplant.
Managing Complications
Preventative Measures
- Proper Surgical Techniques: Ensuring the procedure is performed by a qualified and experienced surgeon.
- Postoperative Care: Following all care instructions closely to prevent infection and reduce the risk of complications.
- Immediate Reporting of Symptoms: Early detection and reporting of any unusual symptoms to the surgeon can prevent complications from worsening.
Treatment Options
- Infections: Treated with antibiotics.
- Excessive Bleeding: Might require a follow-up visit to the surgeon to address the issue.
- Scarring and Unnatural Growth: Surgical revisions or medical treatments may be necessary to correct these issues.
Summary Table: Managing Risks and Complications
| Complication | Preventative Measure | Treatment Option |
|---|---|---|
| Infection | Sterile technique and proper wound care | Antibiotics |
| Bleeding | Careful handling during surgery | Professional intervention if persistent |
| Scarring | Skilled surgical technique, proper patient selection | Possible surgical revision or other treatments |
| Unnatural Hair Growth | Accurate planning and placement of grafts | Corrective procedures |
| Folliculitis | Keeping the area clean and avoiding irritants | Antibiotics and topical treatments |
Understanding these potential risks and how to manage them is crucial for anyone considering hair grafting. By choosing a skilled surgeon and adhering to postoperative care instructions, patients can significantly reduce the likelihood of complications and enhance their overall results.
Recovery and Aftercare
The success of a hair graft procedure is not only dependent on the surgery itself but also on how well the patient manages the recovery and aftercare. This phase is critical to the overall outcome and includes both immediate and long-term care.
Immediate Postoperative Recovery
Timeline for Initial Healing Phase
- First 24 Hours: Patients may experience some tightness, throbbing, or mild pain. The scalp should be kept dry to aid the healing process.
- First Few Days: Swelling may occur, peaking around 2-3 days post-surgery. Any non-dissolvable sutures or staples used in FUT will remain in place.
- First Week: Patients can usually return to non-strenuous work. Scabs may begin to form around the grafts and should be left to fall off naturally.
Instructions for Wound Care and Sleeping Positions
- Wound Care: Keep the surgical area clean and follow the surgeon’s instructions for washing your hair. Avoid touching or picking at the grafts.
- Sleeping Positions: Sleep with your head elevated on pillows to reduce swelling. Avoid any contact with the grafts to prevent dislodgement.
Long-Term Recovery
Expected Timeline for Hair Growth and Final Results
- 2 to 3 Weeks: Transplanted hair will fall out, which is a normal part of the process.
- 3 to 4 Months: New growth will begin, but it may be fine and thin initially.
- 6 to 9 Months: Hair will start to thicken and mature.
- 12 to 18 Months: The full impact of the transplant will be visible.
Follow-up Appointments and Additional Procedures
- Follow-up Appointments: Regular check-ups will be scheduled to monitor progress.
- Additional Procedures: Some patients may require additional sessions to achieve desired density.
Lifestyle Adjustments
Recommendations for Hair Care and Maintenance Post-Transplant
- Gentle Care: Use gentle shampoos and avoid vigorous scrubbing when washing hair.
- Styling: Avoid styling products and heat tools for the first few weeks post-surgery.
Importance of Avoiding Harsh Treatments or Styles
- Chemical Treatments: Coloring, perming, or straightening treatments should be avoided for at least six weeks.
- Tight Hairstyles: Styles that pull on the hair, such as ponytails or braids, should be avoided in the initial months to prevent stress on the grafts.
Summary Table: Recovery and Aftercare
| Recovery Phase | Care Instructions | Expected Milestones |
|---|---|---|
| Immediate Recovery | Keep scalp dry, sleep elevated, manage pain | Swelling subsides, return to work within a week |
| Long-Term Recovery | Regular follow-up, gentle hair care | New hair growth within 3-4 months, maturation by 12-18 months |
| Lifestyle Adjustments | Avoid harsh treatments, gentle styling | Full recovery and styling freedom after several months |
By following these guidelines for recovery and aftercare, patients can help ensure the best possible outcome from their hair graft procedure. It’s important to maintain open communication with the surgical team and adhere to all recommended postoperative instructions.
Cost and Insurance Coverage
When considering hair grafting, it’s essential to understand the various factors that contribute to the overall cost of the procedure. Additionally, it’s important to recognize that most insurance plans do not cover hair grafting, as it is typically considered a cosmetic procedure. However, some clinics may offer financing options to help manage the costs.
Factors Influencing Cost
The cost of hair grafting can vary significantly based on several key factors:
- Extent of Hair Loss: The stage of baldness affects the number of grafts needed2.
- Number of Grafts: More grafts mean a higher cost. Prices can range from Rs. 20 to Rs. 100 per graft in India, with each graft containing 1 to 3 hair follicles125.
- Chosen Technique: FUE and FUT are the primary techniques, with FUE generally being more expensive due to its labor-intensive nature12.
- Surgeon’s Experience: The reputation and skill level of the surgeon can influence the cost4.
- Clinic Location: Costs can vary by region and the clinic’s facilities45.
- Additional Costs: These may include follow-up treatments, medications, and postoperative care12.
Additional Costs
Beyond the initial procedure, patients may incur additional costs:
- Follow-up Treatments: May be necessary to achieve the desired density or to address any complications.
- Medications: Postoperative medications for pain, swelling, or infection prevention.
- Postoperative Care: Special shampoos or treatments to aid in healing and hair growth.
Insurance and Financing
- Insurance Coverage: Hair grafting is usually not covered by insurance as it is deemed cosmetic2.
- Financing Options: Some clinics offer payment plans or financing options to make the procedure more accessible3.
Cost-Effectiveness
- Long-Term Benefits: Hair grafting can provide a permanent solution to hair loss, potentially making it more cost-effective over time compared to ongoing non-surgical treatments.
- Comparison with Other Treatments: Non-surgical options may require continuous expense over time, whereas hair grafting is a one-time cost with lasting results.
Summary Table: Cost Considerations for Hair Grafting
| Cost Factor | Details |
|---|---|
| Extent of Hair Loss | Determines the number of grafts needed, affecting the total cost. |
| Number of Grafts | Cost per graft multiplied by the number of grafts required. |
| Technique | FUE is typically more expensive than FUT. |
| Surgeon and Clinic | Experience and location can influence the price. |
| Additional Costs | Follow-up, medications, and care can add to the overall expense. |
| Insurance and Financing | Procedures are generally not covered by insurance; financing may be available. |
| Cost-Effectiveness | Long-term benefits may outweigh the upfront cost compared to other treatments. |
In conclusion, while the upfront cost of hair grafting can be significant, the long-term benefits of a permanent solution to hair loss may provide value over time. It’s important for patients to consider all factors and potential additional costs when planning for their procedure.